python中的线程与GIL
前言:
-
C python 有GIL 全局解释器锁
-
影响多线程的使用,性能
测试 4 核的 window电脑
import time
def time_need(func):
def inner(*args, **kwargs):
start = time.time()
ret = func(*args, **kwargs)
stop = time.time()
print(stop - start)
return ret
return inner
@time_need
def countdown(n):
while n > 0:
n -= 1
if __name__ == '__main__':
COUNT = 100000000
countdown(COUNT)
时间 4.45 平均
import time
from threading import Thread
def time_need(func):
def inner(*args, **kwargs):
start = time.time()
ret = func(*args, **kwargs)
stop = time.time()
print(stop - start)
return ret
return inner
@time_need
def countdown(n):
while n > 0:
n -= 1
if __name__ == '__main__':
COUNT = 100000000
t1 = Thread(target=countdown, args=(COUNT//2,))
t2 = Thread(target=countdown, args=(COUNT//2,))
t1.start();t2.start()
t1.join();t2.join()
time 15.05
python 的线程
-
系统级别的线程
• Python threads are real system threads • POSIX threads (pthreads) • Windows threads -
主线程控制
• Fully managed by the host operating system -
表示Python解释器进程的线程化执行(是用C编写的)
• Represent threaded execution of the Python interpreter process (written in C)
不能并行执行
GIL 使解释器只有一个线程运行
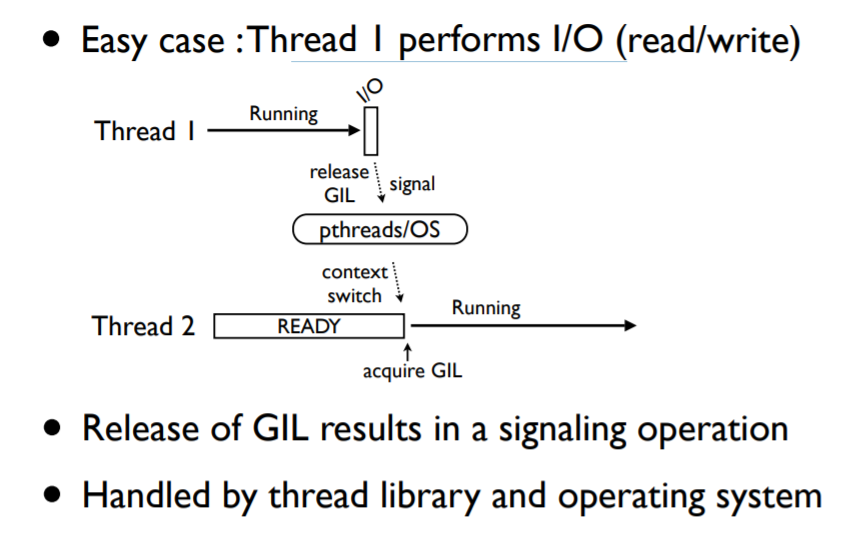
• When a thread is running, it holds the GIL
• GIL released on I/O (read,write,send,recv,etc.)
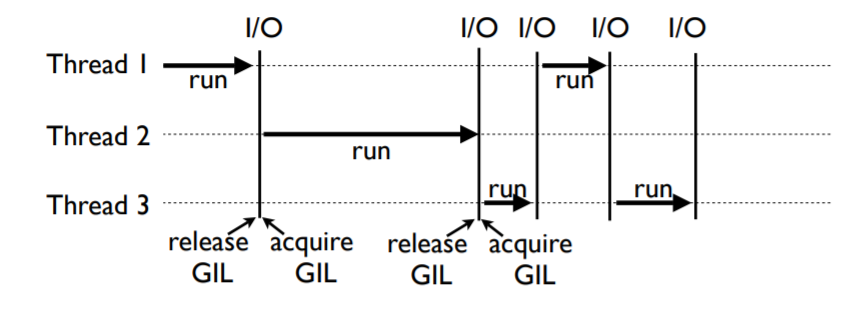
CPU bound 计算密集型 任务
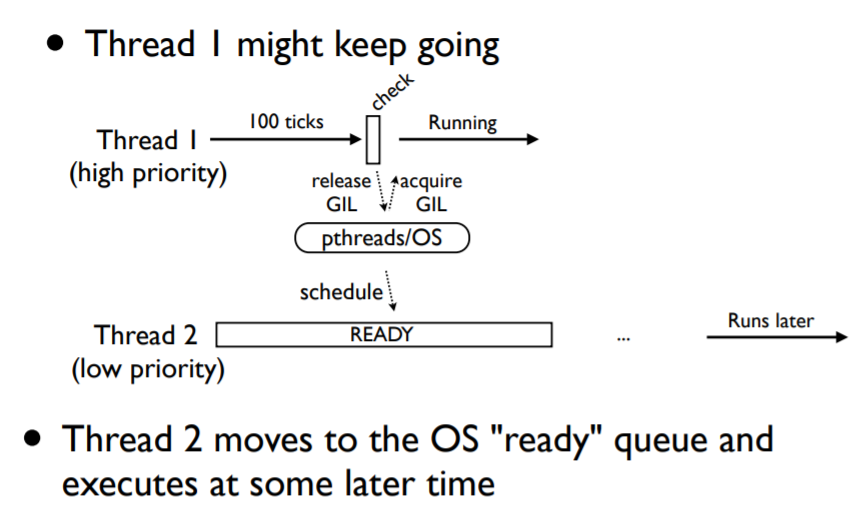
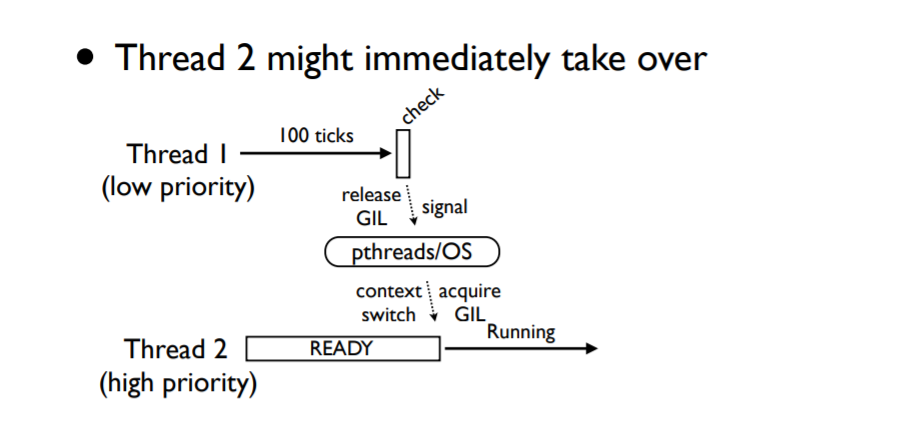
CPU密集型的线程(不会执行IO操作) 会被特殊处理
会周期性的检查,
per check every 100 ticks
通过设置 sys.setcheckinterval() 可以修改周期
ticks 不是时间概念,它对应着python解释器的指令
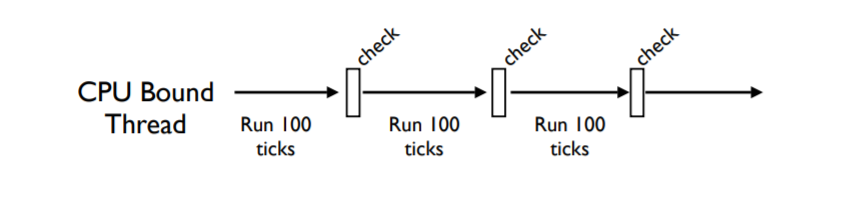
当前运行的线程会执行的周期性动作:
• Resets the tick counter 重置tick counter
• Runs signal handlers if the main thread 主线程会运行 signal handler
• Releases the GIL 释放GIL锁
• Reacquires the GIL 获取GIL锁
GIL 以及 线程切换的原理
(1) python 锁
python 解释器只提供了一种类型的锁 (in C语言), 来构造, 实现 线程同步的原型
不是简单的互斥锁
它是一个由二进制构造的二进制信号量 pthreads互斥锁和 条件变量
锁的结构:
locked = 0 # Lock status
mutex = pthreads_mutex() # Lock for the status
cond = pthreads_cond() # Used for waiting/wakeup
工作模式:
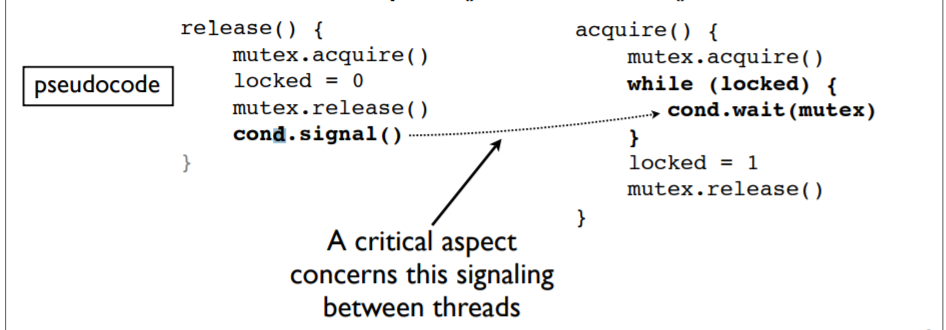
(2) 线程切换