什么时候用 FBV 或者 CBV
流程图:
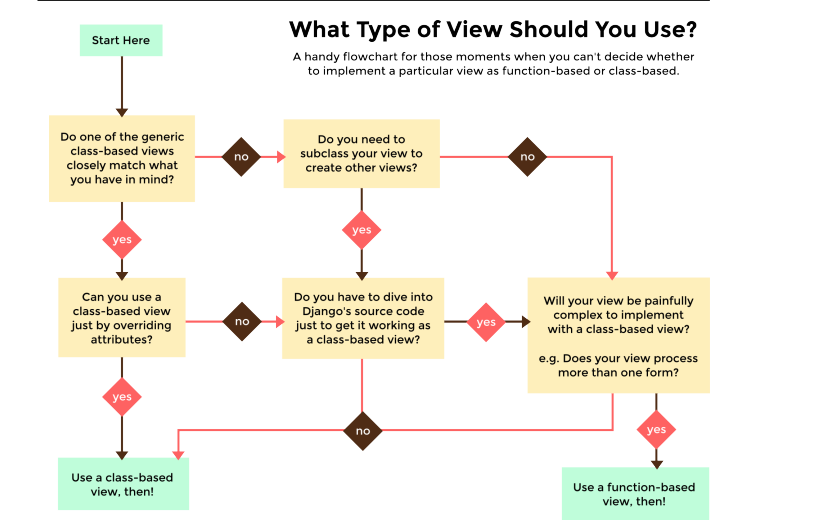
通常情况下使用 CBV, FBV用来补充
FBVs to implement
only the custom error views
or
complicated ones that would be a pain to implement with CBVs.
不要把视图逻辑(View Logic)放在 URLlConfs 中
参考 Django’s URL design philosophy
1 The views modules should contain view logic.
2 The URL modules should contain URL logic.
一个不好的实例 (虽然是官方实例)
# Don't do this!
from django.conf.urls import url
from django.views.generic import DetailView
from tastings.models import Tasting
urlpatterns = [
url(r'^(?P<pk>\d+)/$',
DetailView.as_view(
model=Tasting,
template_name='tastings/detail.html'),
name='detail'),
url(r'^(?P<pk>\d+)/results/$',
DetailView.as_view(
model=Tasting,
template_name='tastings/results.html'),
name='results'),
]
缺点
Loose coupling
1 耦合性太强(model 和 view在一起, 无法重用 view)
Infinite flexibility
2 缺少灵活性
推荐的写法
# app tastings
# tastings/views.py
from django.urls import reverse
from django.views.generic import ListView, DetailView, UpdateView
from .models import Tasting
class TasteListView(ListView):
model = Tasting
class TasteDetailView(DetailView):
model = Tasting
class TasteResultsView(TasteDetailView):
template_name = 'tastings/results.html'
class TasteUpdateView(UpdateView):
model = Tasting
def get_success_url(self):
return reverse('tastings:detail',
kwargs={'pk': self.object.pk})
# tastings/urls.py
from . import views
urlpatterns = [
url(
regex=r'^$',
view=views.TasteListView.as_view(),
name='list'
),
url(
regex=r'^(?P<pk>\d+)/$',
view=views.TasteDetailView.as_view(),
name='detail'
),
url(
regex=r'^(?P<pk>\d+)/results/$',
view=views.TasteResultsView.as_view(),
name='results'
),
url(
regex=r'^(?P<pk>\d+)/update/$',
view=views.TasteUpdateView.as_view(),
name='update'
)
]
使用 URL Namespace
在项目根目录下 urls.py
urlpatterns += [
url(r'^tastings/', include('tastings.urls', namespace='tastings')),
]
在 app tastings 中就可以使用 namespace
# tastings/views.py snippet
class TasteUpdateView(UpdateView):
model = Tasting
def get_success_url(self):
return reverse('tastings:detail',
kwargs={'pk': self.object.pk})
# taste_list.html
{ extends 'base.html' }
{ block title }Tastings{ endblock title }
{ block content }
<ul>
{ for taste in tastings }
<li>
<a href="{ url 'tastings:detail' taste.pk }"></a>
<small>
(<a href="{ url 'tastings:update' taste.pk }">update</a>)
</small>
</li>
{ endfor }
</ul>
{ endblock content }
Django 的 views 是函数
Django的views实际是接收(HTTP request object)的函数, 然后返回HTTP response object
# Django FBV as a function
HttpResponse = view(HttpRequest)
# Deciphered into basic math (remember functions from algebra?)
y = f(x)
# ... and then translated into a CBV example
HttpResponse = View.as_view()(HttpRequest)
- 最简单的视图
# The simplest FBV
def simplest_view(request):
# Business logic goes here
return HttpResponse('FBV')
# The simplest CBV
class SimplestView(View):
def get(self, request, *args, **kwargs):
# Business logic goes here
return HttpResponse('CBV')
不要在views中使用 locals()
# date
def ice_cream_store_display(request, store_id):
store = get_object_or_404(Store, id=store_id)
date = timezone.now()
return render(request, 'melted_ice_cream_report.html', locals())
# now
def ice_cream_store_display(request, store_id):
store = get_object_or_404(Store, id=store_id)
now = timezone.now()
return render(request, 'melted_ice_cream_report.html', locals())
# 这里的now与函数now命名冲突
正确的写法
def ice_cream_store_display(request, store_id):
return render(
request,
'melted_ice_cream_report.html',
{
'store': get_object_or_404(Store, id=store_id),
'now': timezone.now()
}
)
