FastAPI has a very powerful but intuitive — Dependency Injection system.
FastAPI 有一个 强大且直观的 依赖注入系统
基本概念
Dependency 的作用
Have shared logic (the same code logic again and again).
逻辑代码复用
Share database connections.
共享数据库连接
Enforce security, authentication, role requirements, etc.
强制 安全, 认证, 角色权限等 中间件
And many other things...
...
怎样定义一个 dependency
The key factor is that a dependency should be a "callable".
所以 dependency 可以是:
1 函数 getCommonQueryParams()
2 类 CommonQueryParams()
example 1 复用相同的 param 参数
from fastapi import Depends, FastAPI, Path, Query
app = FastAPI()
async def common_parameters(q: str = Query(...), skip: int = Query(...), limit: int = Query(None)):
return {"q": q, "skip": skip, "limit": limit}
# 一个接收 path路由函数需要的 相同param参数的 函数
@app.get("/items/")
async def read_items(commons: dict = Depends(common_parameters)):
return commons
@app.get("/users/")
async def read_users(commons: dict = Depends(common_parameters)):
return commons
example 2 复用相同的 param 参数
使用类定义 dependency
from fastapi import Depends, FastAPI, Query
app = FastAPI()
fake_items_db = [{"item_name": "Foo"}, {"item_name": "Bar"}, {"item_name": "Baz"}]
class CommonQueryParams(object):
def __init__(self, q: str = Query(...), skip: int = Query(...), limit: int = 100):
self.q = q
self.skip = skip
self.limit = limit
@app.get("/items/")
async def read_items(commons: CommonQueryParams = Depends(CommonQueryParams)):
# async def read_items(commons = Depends(CommonQueryParams)):
# async def read_items(commons: CommonQueryParams = Depends()):
response = {}
if commons.q:
response.update({"q": commons.q})
items = fake_items_db[commons.skip : commons.skip + commons.limit]
response.update({"items": items})
return response
多层的 dependency
from fastapi import Cookie, Depends, FastAPI, Path, Query
app = FastAPI()
async def query_extractor(q: str = Query(None )):
return q
async def query_or_cookie_extractor(
q: str = Depends(query_extractor), cookie: str = Cookie(...)
):
if not q:
return cookie
return q
@app.get("/items/")
async def read_query(query_or_cookie: str = Depends(query_or_cookie_extractor)):
return {"q_or_cookie": query_or_cookie}
# curl -X GET "http://127.0.0.1:8002/items/?q=q" -H "accept: application/json" -H "Cookie: cookie=cookie"
path路由装饰器中的 Dependencies
The path operation decorator receives an optional argument dependencies
@app.get("/items/", dependencies=[Depends(verify_token), Depends(verify_key)])
dependency 可以用来raise Exception 和 return value
from fastapi import Depends, FastAPI, Header, HTTPException
app = FastAPI()
async def verify_token(x_token: str = Header(...)):
if x_token != "fake-super-secret-token":
raise HTTPException(status_code=400, detail="X-Token header invalid")
# raise
async def verify_key(x_key: str = Header(...)):
if x_key != "fake-super-secret-key":
raise HTTPException(status_code=400, detail="X-Key header invalid")
return x_key
# return
@app.get("/items/", dependencies=[Depends(verify_token), Depends(verify_key)])
async def read_items(x_item: str = Depends(verify_key)):
print(x_item)
return [{"item": "Foo"}, {"item": "Bar"}]
# curl -X GET "http://127.0.0.1:8002/items/"
# -H "accept: application/json"
# -H "x-token: fake-super-secret-token"
# -H "x-key: fake-super-secret-key"
通过 yield 使 dependencies 用来 extra steps
sometimes also called
"exit",
"cleanup",
"teardown",
"close",
"context managers",
...
python3.6 需要下载
pip install async-exit-stack async-generator
或者使用 python3.7+
数据库依赖 实例
async def get_db():
db = DBSession()
try:
yield db
finally:
db.close()
(1) 这部分代码, 会在发送 response 之前执行
=======(1)========
db = DBSession()
try:
yield db
=================
(2) 这部分代码, 这里是注入到 denpendecy中的 value
=======(2)========
yield db
=================
(3) 这部分会在 response 发送后执行
=======(3)========
finally:
db.close()
=================
Sub-dependencieswithyield
from fastapi import Depends
async def dependency_a():
dep_a = generate_dep_a()
try:
yield dep_a
finally:
dep_a.close()
async def dependency_b(dep_a=Depends(dependency_a)):
dep_b = generate_dep_b()
try:
yield dep_b
finally:
dep_b.close(dep_a)
async def dependency_c(dep_b=Depends(dependency_b)):
dep_c = generate_dep_c()
try:
yield dep_c
finally:
dep_c.close(dep_b)
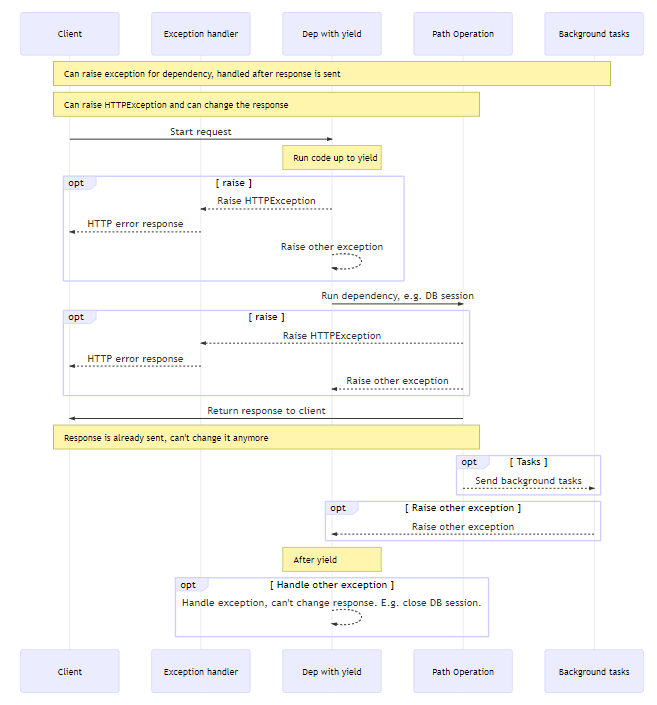
dependency 异常处理流程
The exit code in dependencies with yield is executed after Exception Handlers.
There’s nothing catching exceptions thrown by your dependencies in the exit code (after the yield).
上下文管理器 实现
class MySuperContextManager:
def __init__(self):
self.db = DBSession()
def __enter__(self):
return self.db
def __exit__(self, exc_type, exc_value, traceback):
self.db.close()
async def get_db():
with MySuperContextManager() as db:
yield db
